Yellow Leaves on Marijuana Plants
Marijuana yellow leaves are a common issue that home growers often face. The most important thing that the grower must address is identifying the causes behind this problem and understanding the potential impact on the grow operation. That’s why at Sweet Seeds®, we’re here to explain the possible causes and solutions for marijuana yellow leaves.
In most cases, the appearance of yellow leaves in cannabis represents a sign that there is some problem with your plant. However, it isn’t always a reason to worry. Below, we explain the main reasons why this may happen to the cannabis plant and how to fix it.
If you’ve ever noticed marijuana yellow leaves on your plant, please keep reading because this article is for you!
Causes of Marijuana Yellow Leaves
Marijuana yellow leaves can appear for various reasons, such as poor pH regulation, which prevents proper mineral absorption, overwatering, or nutrient deficiencies, among many others. All these factors indicate that your plant isn’t producing enough chlorophyll and is not able to carry out photosynthesis correctly.
This symptom can be a clear sign that something isn’t right and needs to be addressed. To help you detect and solve the issue, we’ll break down each potential cause. In the end, you’ll see that in some specific cases, marijuana yellow leaves can be a natural and even desired part of the plant’s growth cycle.
1. Lack or Excess of Watering
Both overwatering and underwatering can lead to marijuana yellow leaves. In either case, the solution is in your hands. You just need to determine the right amount of water your plants need and the ideal time to water them. Watering small plants with a limited root system is different from watering large, mature plants.
Here are some symptoms of overwatering or underwatering that you might notice if your watering routine isn’t ideal, causing your marijuana plants to develop yellow leaves:
- Drooping leaves: If this happens, check if the pot feels heavy or if the soil is dry to assess whether the plant needs watering or not.
- Pale and thin leaves: This is a clear sign of underwatering. This issue often appears unevenly across the plant, unlike in the case of overwatering.
- Yellow leaves throughout the plant: When the yellowing is widespread throughout the whole plant, it usually indicates overwatering.
To avoid watering issues in your plants, we recommend the following:
- Use high-quality substrates to ensure better drainage for your plants. You can improve drainage by adding perlite or clay pebbles to the soil mix or even placing river stones at the bottom of the pot.
- Choose pots that are suitable for the size of your plant. Air pots, for example, enhance root oxygenation and help prevent waterlogging.
- Avoid continuous overwatering, as it can weaken your cannabis plants, reduce root aeration, and lead to fungal contamination in the roots. It’s crucial to allow dry periods between waterings, but without causing water stress, as it would make the leaves lose their firmness as a result of the lack of moisture.
As a general guideline, for a standard 1 m² grow area with optimal conditions and 7L pots, small plants typically need about 0.5 liters of water every 4 or 5 days. In contrast, mature and well-developed plants can handle about 1 liter every 2 or 3 days.
A useful rule of thumb is to water with just a little bit over 10% of the total volume of the pot. For example, a 7L pot with a mature plant would need around 0.8 liters of nutrient solution. Always remember to lift the pot before watering to get a feel for its weight when moist versus dry, so that you can get used to evaluate this in future occasions.
It’s best to avoid watering until at least the top 2 centimeters of soil have completely dried out.
While optimal watering is key, marijuana plants are quite drought tolerant. It’s better to let them go slightly thirsty for a day or two than to expose them to continuous excess moisture, which can have disastrous consequences for your cannabis plants.
However, severe droughts that cause intense water stress can also damage your plants by killing a large portion of the root system, severely limiting their ability to absorb water and nutrients.
Additionally, extreme drought can degrade the quality of the substrate, reducing its ability to retain water and leading to the loss of much of its beneficial microbiological life, such as fungi and bacteria.
2. Excessive Light
Another common cause of marijuana yellow leaves is exposing plants to excessive light. This often happens when grow lights are placed too close to the plants. Intense lighting systems like LEC or HPS are known for causing burns to the leaves and flowers of the cannabis plant, but even LEDs (despite producing less heat) can still cause light stress due to their extremely high intensity.
Yellowing or chlorosis on the upper parts of the plant typically appears when the leaves are overworked in a short period. Remember, marijuana can only absorb a limited amount of lumens, and when that threshold is exceeded, the plants may show signs of burns or chlorosis. Here’s a general guide to the ideal light levels for each growth stage:
- Clones / young plants: 5,000-10,000 Lux (lm/m²)
- Vegetative Stage: 15,000-50,000 Lux
- Flowering stage: 50,000-75,000 Lux
To measure light intensity, you can use tools like a lux meter or a photometer. A photometer is an instrument commonly used in photography to measure scene lighting. There are also smartphone apps that, while less accurate, can still be a quite helpful tool for cannabis home growers.
To fix light-related yellowing, simply increase the distance between the grow lights and the affected plants. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines to avoid giving either too much or too little light. Keep in mind that insufficient light can also lead to pale, weak leaves.
3. Potassium Deficiency
Potassium is one of the most crucial nutrients for marijuana plants, acting as a catalyst in several key metabolic processes, including the following:
- Photosynthesis.
- Protein and amino acid synthesis.
- Increasing bud size, density, and weight.
- Boosting the plant’s overall strength and resilience.
- Enhancing root hardness and durability (when combined with phosphorus).
- Providing frost resistance by acting as a natural antifreeze.
- Supporting terpene production.
Symptoms of potassium deficiency in marijuana plants include:
- Chlorosis (yellowing) of older leaves, making them appear pale and discolored.
- Yellowing at the tips and edges of the leaves, which may spread across the entire leaf with time.
- The plant shows weakness and low resilience to adversities.
- Thin, fragile stems that break easily.
How to fix potassium deficiency:
- Use fertilizers rich in potassium or opt for a specific supplement designed to correct deficiencies. Always follow the manufacturer’s dosage recommendations, as overuse can cause nutrient lockout.
- Monitor calcium and nitrogen levels, as excessive amounts of these nutrients could also be a problem as they can contribute to lower potassium absorption.
- If you suspect salt is building up in the substrate and it may be blocking nutrient uptake, perform a root flush and follow up with high-quality nutrients containing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
- Wait for your plant to recover and then closely observe and control new leaf growth to ensure the problem has been totally resolved.
4. Nitrogen Deficiency
When your beloved cannabis plants suffer from a nitrogen deficiency, one of the first signs is the appearance of yellow spots and overall discoloration on the underside of the lower leaves. These leaves often feel soft to the touch and fall off easily, sometimes even on their own. Nitrogen deficiency typically occurs during the vegetative stage or at the start of the flowering stage.
Commonsymptoms of nitrogen deficiency in marijuana plants may include the following:
- The lower leaves of the plant turn pale and eventually develop yellow spots before falling off in large numbers.
- The yellowing can spread upward throughout the entire plant, as it pulls nutrients from older leaves to sustain new growth.
- The affected leaves may curl or distort in shape.
- The plant often lacks its usual healthy shine.
- Premature flowering may occur, resulting in smaller plants and lower yields.
If you want to fix the problem of marijuana yellow leaves due to nitrogen deficiency, take note of the following advice:
- Make sure that you only use nutrient-rich fertilizers that contain adequate nitrogen to support healthy growth for cannabis plants.
- Repot your cannabis plant into a larger container with fresh, well-aerated soil. This not only provides new nutrients to the plant, but it also encourages stronger root development.
- Incorporate water-soluble nitrogen into your watering routine. This helps the roots absorb nitrogen more effectively, allowing the plant to regain its vibrant green color.
- Grow symbiotic plants alongside your cannabis plants. Other plants like legumes, form natural partnerships with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, enriching the soil with bioavailable nitrogen and boosting overall plant health.
- Monitor your grow daily. An early detection of nitrogen deficiency allows for quicker recovery and minimizes potential damage to the plant.
- Expect about a week for the plant to bounce back after correcting the nitrogen levels. However, keep in mind that leaves that already turned yellowed will not recover and should be pruned at some point to improve airflow and plant appearance.
- For outdoor grows, regularly applying compost can naturally enrich the soil and help prevent future deficiencies.
5. Causes of Yellowing Due to Nutrient Absorption Blockages
Excessive Amounts of Salts in the Soil
This can be caused by using water with a high salt content, or due to excessive fertilizer use, especially in potted plants or reused substrates. Excess salts can accumulate in the growing medium, interfering with the roots’ ability to absorb all the nutrients, leading to leaf discoloration, spots, or burns in our cannabis plants.
Reused Soil or Soil from Previous Grows
In the case of reused soil or areas where multiple grows have taken place, residual salt and nutrient buildup can negatively impact absorption, resulting in the same issues mentioned above.
Excess Fertilizers
Applying too many fertilizers, or the use of unbalanced fertilizers can lead to nutrient absorption blockages. This can cause partial or widespread yellowing, burns, spots, and leaf deformities.
Possible Solutions
1. Root flushing in pots
- Performing a root flush in pots involves thoroughly watering the plants to eliminate excess salts accumulated in the substrate.
- Adding enzymes to the substrate can help break down organic residues and salts, making the flushing process more effective.
2. Adjusting watering and fertilization
- EC control of water: Use water with an appropriate EC level to prevent excessive salt buildup in your soil mix.
- Balanced fertilization: Ensure fertilizers are applied in a balanced way, following the recommendations for the plant’s specific growth stage.
3. Outdoor grows in soil
- Although more challenging in outdoor grows in soil, flushing can help reduce salt accumulation. However, its effectiveness may be more limited when compared to potted plants.
4. Continuous monitoring
- Soil analysis: Conduct regular soil tests to assess salt and nutrient concentrations and adjust growing practices accordingly.
It’s crucial to tailor these solutions to the specific conditions of your grow and continuously monitor plant health to prevent recurring issues that could affect the health of your cannabis leaves.
6. Inadequate Temperature
As we know, temperature and ambient humidity, along with CO₂ levels, light, water, and nutrients, are key factors for the proper development of marijuana plants. Depending on the specific conditions of each grow operation, you may encounter low or very high temperatures, as well as relative humidity levels outside of the optimal range.

- Temperatures below 10°C can be one of the reasons why marijuana yellow leaves appear.
- The solution for indoor grows is as simple as increasing the temperature in the grow space. You can use electric blankets, heaters, or increase the lighting power in the room.
- If you are growing cannabis outdoors, you will need to protect the plants with plastic covers or use a greenhouse.
- Extremely high temperatures will also cause the leaves to turn yellow and dry out.
- If the temperature exceeds 28°C, it can limit the plant’s photosynthesis, affecting its normal development.
- For indoor grows, besides increasing air extraction, you can add more fans or use an air conditioner to lower the temperature and improve air circulation.
- For outdoor grows, make sure to provide some shade for the plants. You can use agricultural shade nets, and if you’re growing in pots, it’s advisable to use light-colored ones to reflect sunlight. Alternatively, you can shade the pots with cardboard or similar materials to prevent direct sun exposure and protect the roots.
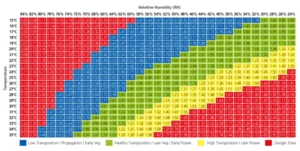
- The Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD) is the difference between the water vapor present in the air and its saturation point, determined by temperature, wind speed, and relative humidity. In dry and warm environments, plants transpire more and close their stomata to conserve water, which can lead to burns and discoloration in the leaves of the cannabis plant.
- In cold and humid conditions, a low VPD can cause stomata closure, water accumulation on the leaves, and an increased risk of suffocation and attacks from opportunistic fungi.
- Here’s a chart to help you understand the ideal balance between humidity and temperature.
Other causes
In addition to the causes already mentioned along this article, there are other reasons why your cannabis plant may develop yellow leaves. These include the following:
- The appearance of pests and diseases such as septoria, thrips, fungus gnats, etc.
- The use of poor-quality substrates. This can be a major issue for the grow, as the soil may lack proper aeration and have insufficient drainage.
- Root rot. In this case, yellow leaves are a symptom of a microbial disease affecting the plant’s root system.
- Nutritional deficiencies of other essential nutrients, such as iron or magnesium, which can also cause yellowing of cannabis leaves in your plants.
Solutions for Marijuana Yellow Leaves
Once you have identified the issue causing yellow leaves in your cannabis plant, it becomes essential to act as quickly as possible to solve this problem.
Below you can find the steps that you should follow to solve the problem based on where the yellow leaves appear:
New Yellow Leaves
Immobile nutrients in plants are those that do not easily redistribute once absorbed. This means they mainly affect the actively growing parts of the plant during nutrient uptake.
Here are some examples of immobile nutrients and the parts of the plant where they typically impact:
- Calcium (Ca): Mainly affects the parts of the plant that are growing, like root tips and new shoot growth points.
- Boro (B): Crucial for growth points and the development of new tissues, including flower and fruit formation.
- Iron (Fe): Often affects young leaves, as immobile iron deficiency appears in the newest parts of the plant.
- Manganese (Mn): Deficiency can negatively impact growing tips and young leaves.
These immobile nutrients are vital for various functions of the cannabis plant, and their deficiencies generally appear in the newest, most active growth areas of the plant. To address deficiencies, it is very important to use balanced fertilizers and to carefully correct any issues with the substrate or irrigation water.
Also, make sure that your plants receive adequate light for proper photosynthesis.
It is also important to monitor chlorine levels in the water, as excess chlorine can cause iron chlorosis. Additionally, avoid overwatering your plants.
Yellowing on the Tip of the Leaves
To tackle this issue, it’s crucial to identify the specific cause of the problem.
Make sure to adjust nutrient levels, as over-fertilization often first shows through burnt leaf tips.
Check and correct pH levels, monitor water quality, and maintain proper environmental conditions to help resolve yellowing tips.
Marijuana Yellow Leaves in the Lower Part of the Plant
Mobile nutrients in plants can be redistributed once absorbed. This means that, in case of deficiency, the plant transfers these nutrients from older leaves to younger leaves to keep adequate growth. Here are some examples of mobile nutrients and the parts of the plant that are typically affected by their deficiency:
- Nitrogen (N): A nitrogen deficiency first affects older leaves as the plant reallocates nitrogen from these leaves to newer growth spots.
- Phosphorus (P): A phosphorus deficiency often targets older leaves and, during the flowering stage, can impact flower and fruit development.
- Potassium (K): Potassium deficiencies usually start in older leaves and can spread to younger leaves as well.
- Magnesium (Mg): Lacking magnesium is first evident in older leaves, since it can be moved to younger partes of the plant.
Deficiencies of mobile nutrients generally show up in the older parts of the plant. This happens because the plant prioritizes the use of these nutrients to parts where newer growth is active. To fix these issues, always make sure to provide balanced nutrients and adjust fertilization practices according to the plant’s needs.
Regarding temperature, make sure to monitor the ranges mentioned earlier and use materials or tools as needed to regulate it.
Yellow-Spotted Leaves
Pests, fungi, and even rodents must be controlled, and above all, their appearance should be prevented. Keep your grow space clean and regularly inspect your plants to detect any potential infestations early.
Tips to Prevent Marijuana Yellow Leaves
As we always say at Sweet Seeds®, prevention is the best form of defense. Here are some tips to help avoid yellow leaves on your cannabis plants.
- Define your type of grow and choose the right genetics. At Sweet Seeds®, we’ve developed our entire catalog to suit both indoor and outdoor grows. Adapt and adjust your watering accordingly.
- Ensure your cannabis plants receive all the necessary care throughout their entire life cycle.
- Clearly understand the essential nutrients your plants need.
- Carefully control light exposure.
- Make sure to maintain appropriate temperature and humidity levels in your vegetative and flowering rooms.
Non-Problematic Marijuana Yellow Leaves
While this article has focused on the issues that can cause yellow leaves on cannabis plants, yellowing isn’t always a reason for concern. Yellow leaves can also be a natural part of the plant’s life cycle. It’s normal for plants to shed older leaves, especially during the final stages of the grow.
The Final Stage of Flowering
During the flowering stage, it is quite common that the cannabis plant focuses most of its energy on bud production. As the end of flowering approaches and harvest time nears, it’s quite usual for the leaves to turn yellow, and this doesn’t necessarily signal a problem.
In indoor grows, it’s advisable to remove dead leaves to prevent the buildup of decomposing organic matter, which can become a breeding ground for fungi and pathogens in our cannabis plants.
Instead of throwing the leaves away, consider composting them. Composting improves soil structure and naturally enriches it with nutrients for future grows. In outdoor grows, this is a common practice that offers both savings and great benefits.
After Flushing the Roots

Flushing the roots near the end of flowering can also cause the leaves to turn yellow and eventually fall off.
Realizar un lavado de raíces produce una limitación en el aporte de nutrientes, limpiando el sustrato de sales acumuladas y obligando a la planta a consumir el alimento de su reserva en las hojas, lo que afecta positivamente a un mejor sabor y calidad de los cogollos.
Contact Sweet Seeds®
Now you have all the information you need to manage and save your cannabis plants from undesired yellow leaves.
After reading this article, if you find yourself considering expanding your cannabis seed collection, Sweet Seeds® offers a wide range of top-quality seeds: autoflowering seeds, photoperiod-dependent seeds, F1 Fast Version® seeds, The Red Family seeds, CBD seeds… and much more!
Through the Sweet Seeds® online forum, our expert growers are ready to provide all the help you might need. They’ll assist you in resolving any issues your cannabis plants may face during their entire life cycle. We look forward to seeing you there!
Sweet Seeds S.L. is not responsible for any misuse of the information provided in this article. Growing Cannabis may constitute a criminal offense or administrative infraction; please check the Cannabis legislation applicable in your place of residence. Sweet Seeds S.L. does not, under any circumstances, intend to promote illegal practices.
- How to Use Bat Guano in Cannabis Cultivation - 25 de February de 2026
- Sweet Cheese XL Auto® Grow Diary - 24 de December de 2025
- Sweet Cheese® Grow Diary - 24 de December de 2025